Sphinx
Contents
Sphinx#
Tips & Tricks#
Useful Extensions#
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
links to external Sphinx documentations of
functions and classes,
e.g. |
|
provides container element with different tabs beside each other |
|
create a list of all todos |
|
support for Google-style docstrings |
|
create HTML pages showing the source code and add links to them to the respective objects in the source code documentation |
|
include code snippets/examples in |
|
given a Python module/class/function, automatically create the source code documentation |
|
just point Sphinx to the Python modules and it
will generate the stub files for
|
|
creates summary tables for the classes and functions in a module |
|
automatic documentation of typehints,
must be listed after |
|
add |
|
create one or more galleries of examples and plots from folders containing Python scripts and automatically cross-reference them from the source code documentation |
|
adds a copy button to code snippets |
|
creates |
|
screen-size responsive web-components based on Bootstrap, such as badges and buttons |
Built-in extensions are listed here: https://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/master/usage/extensions/index.html
Text After Roles Without Intermediate Space#
When a role is inserted, such as :class:`pandas.DataFrame`, the backtick
ending the role has to be followed by whitespace. When this is not desired,
e.g. when using the plural, this can be avoided by using a backslash instead
of the space: :class:`pandas.DataFrame`\s will be rendered as
pandas.DataFrames.
Glossary#
The built-in glossary can be generated with the .. glossary:: directive.
Underneath it, the individual terms can be defined like this:
.. glossary::
FPR
False Positive Rate
TPR
True Positive Rate
On a normal rst page, an expression can be linked to the corresponding
glossary entry by means of the :term: role: The code :term:`FPR`
will result in a link like this: FPR. You can also show different
text while still linking to the desired glossary entry: The code
:term:`False Positive Rate <FPR>` will be rendered as False Positive
Rate.
Unfortunately, since rst roles cannot be nested, vanilla Sphinx does not allow for the combination of hovering tooltips with links to a central glossary.
Numbered Footnotes#
I found this great paper [#fPaper]_
.. rubric:: Links
.. [#fPaper] Awesome Authors: *Awesome Paper*, Awesome Journal
is rendered as
Tables#
In simple tables, coded like this
============ ============
Column 1 Column 2
============ ============
row 1 cell 1 row 1 cell 2
row 2 cell 1 row 2 cell 2
============ ============
the relative size of the columns is defined in the <colgroup> and <col>
tags in the generated HTML. The fractions that each column make up are
calculated from the relative length of the === sequences in the rst code.
The Book Theme#
The Book theme is a responsive Sphinx theme with a file-based navigation bar on the left and an in-document table of content in the right page margin.
Homepage: https://sphinx-book-theme.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html
Conda package
sphinx-book-theme: https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/sphinx-book-theme
Warning
At least sphinx-book-theme versions 0.0.40 and 0.0.41 do not
work properly with Sphinx version 4: The .. margin:: and
.. sidebar:: directives are not rendered correctly. This can be fixed
by sticking to sphinx version 3.5.4.
Changing the Page Width#
To increase the width of the overall page, add a custom *.css file to
the _static folder and specify it in conf.py:
html_static_path = ['_static']
html_css_files = ['custom-book.css']
The main container is container-xl. The following snippet will extend the
page over the full width of the browser window. The left sidebar and the right
page margin are kept fixed and the increase in size benefits entirely the
central content pane.
.container-xl {
max-width: none; /* 90% !important; */
}
Page Elements#
Some text in between
- A Caption
Some more text in between
Note
This is a note in the main text
Let’s write some more nonsensical text to simulate a meaningful document containing really great content. Apparently, one has to be careful and watch how the elements in the main text and in the right page margin are laid out. As stated in the Sphinx Book Theme documentation, the elements can overlap.
# now let's see how source code is rendered
import spellbook.python.plot as sb.plot
Any element can be made to extend fully from the main text into the right
page margin by adding :class: full-width.
Note
This is a full-width note
Now the main text continues.
Inline Markup#
GUI labels:
:guilabel:`some-labelrenders as some-labelkeybindings:
:kbd:`Cmd + Shift + Arenders as Cmd + Shift + A
Additional Container Elements#
Tooltips#
There is built-in support for simple tooltips in Sphinx with the :abbr:
role: :abbr:`normal text (tooltip text)` will be rendered as
normal text.
sphinx-tabs#
sphinx-tabs provides the .. tabs:: directive which creates an element
with multiple tabs/pages beside each other
Content of the first tab
Note
Some information can go inside a note
There is some text here
print('... and some code!')
Source Code Documentation#
sphinx.ext.intersphinx#
When make html is run, Sphinx not only creates the HTML pages, but also
the objects.inv in the same directory. The objects.inv files of other
projects can be targeted with intersphinx and used to generate hyperlinks
to the source code documentation of other projects.
Add to conf.py:
intersphinx_mapping = {
'matplotlib': ('https://matplotlib.org/stable/', None),
'numpy': ('https://numpy.org/doc/stable/', None),
'pandas': ('https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/', None),
'python': ('https://docs.python.org/3/', None),
'seaborn': ('https://seaborn.pydata.org/', None),
'tensorflow': ( # https://github.com/GPflow/tensorflow-intersphinx/
# - mentioned in https://stackoverflow.com/a/37444321
'https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python',
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GPflow/tensorflow-intersphinx/master/tf2_py_objects.inv'
)
}
Then, objects belonging to these other projects can be referenced and linked
using the :func: and :class: roles. The following naming prefixes
have to be used:
matplotlibnumpypandasno prefix for Python
seabornsklearnfor scikit-learntffor TensorFlow, e.g.tf.data.Dataset
Note
At least for pandas and TensorFlow, some object names are
expanded in the auto-generated source code documentation based on
the type hints / signatures (but not when the same objects are
mentioned manually in the docstrings with :func: or :class:,
and neither in normal *.rst files!). As a result, the expanded
object names cannot be found in the respective objects.inv
and no external documentation link is added.
For example, :class:`tf.data.Dataset` is rendered correctly
as tf.data.Dataset, but when a signature includes
tf.data.Dataset, this name is expanded to
tensorflow.python.data.ops.dataset_ops.DatasetV2.
Another example is pd.DataFrame which is expanded to
pandas.core.frame.DataFrame.
This is a known issue without any obvious solution on the implementation side: https://github.com/agronholm/sphinx-autodoc-typehints/issues/47
It is possible, however, to fix these special cases by manually writing the types in the docstring:
For parameter types, add the reference in parentheses to the respective parameter (the others remain unaffected), e.g. like so:
Args: data(:class:`pandas.DataFrame`): The dataset
For the return type, just write something like this into the docstring:
Returns: Tuple of :class:`tf.data.Dataset`: A tuple containing the training and validation (and possibly test) datasets
sphinx.ext.doctest#
Directives:
Test code separated from the output
.. testcode:: import numpy as np a = np.arange(10) print(a.shape) Output: .. testoutput:: (10,)
Test code interleaved with the output
.. doctest:: >>> print('hello world!') hello world! >>> print('hello again...') hello again...
Run with make doctest.
Links
sphinx-autodoc-typehints#
sphinx-autodoc-typehints automatically generates the documentation of the typehints, thus eliminating the need to manually reproduce the typehints in the docstrings.
Note
When used together with sphinx.ext.napoleon,
sphinx-autodoc-typehints has to be included after
sphinx.ext.napoleon in the configuration file conf.py
Settings:
typehints_fully_qualified = True: show the module names before the object namessimplify_optional_unions = False: keep typing.Optional in Unions for optional parameters, I find this more explicit
Links
Tools for Jupyter Notebooks#
nbsphinx#
The nbsphinx extension provides support for Jupyter notebooks in Sphinx. Notebooks can be included in toctrees and will be exectuted when Sphinx is run. The rendered text and code cells along with the resulting output will be added to the documentation.
Conda package
nbsphinx: https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/nbsphinx
Quickstart:
Add
'nbsphinx'to theextensionslist inconf.pyAdd some
*.ipynbfiles to a toctreeRun
make htmlto create the documentation
sphinx-thebe#
sphinx-thebe is a Sphinx extension for live code execution.
My Modifications and Additions#
Admonitions#
General Blue Admonition#
Blue Admonition
.. admonition:: Admonition Title
:class: spellbook-admonition-blue
Admonition content
General Orange Admonition#
Orange Admonition
.. admonition:: Admonition Title
:class: spellbook-admonition-orange
Admonition content
Definition Admonition#
Definition
.. admonition:: Definition
:class: spellbook-definition
Definition content
Glossary Tooltips#
Definition
Modified behaviour of the :term: and :abbr: roles.
The :term:`type-1 error` is related to the :abbr:`CL (confidence level)`.
As mentioned in Glossary, Vanilla Sphinx has the limitation
that reST roles cannot be nested and therefore a word or phrase cannot be
simultaneously given a tooltip with :abbr:`phrase` and entered and linked
to the glossary with :term:`phrase`.
To overcome this, I extended the behaviour of the :term: role.
The Python module source/_static/glossary.py is invoked in the
Makefile after the sphinx-build command. It parses
the automatically created glossary in build/html/glossary.html and extracts
the terms and their definitions/explanations into a JSON dictionary which is
then written to build/html/_static/glossary.json. Despite the name, this
file is actually a bit of JavaScript just containing the JSON dictionary.
glossary.json is added to the html_js_files configuration parameter in
source/conf.py so that this file is added as a script and read when an HTML
page is loaded. I also wrote a JavaScript script source/_static/tooltip.js
that is also added to the HTML pages. When the HTML page is loaded, it reads
the JSON glossary dictionary from glossary.json and creates event handlers
connected to the all the appearances of the glossary terms on the HTML page.
When the mouse is then brought to hover over such a link to a glossary term,
the corresponding entry is retrieved from the glossary dictionary and displayed
in a custom tooltip. These tooltips are styled in
source/_static/tooltip.css. The regular hyperlinks of the terms/phrases to
their coresponding entries in glossary.html are retained, so when clicking
on a term/phrase, the full glossary is still loaded.
These glossary tooltips support all the normal reST containers, directives
and roles and therefore, the glossary entries can be written without
limitations. Since normally, links to the MathJax library are only included
in the HTML headers, when the underlying *.rst file contains a math
directive or role, I had to force the inclusion of the corresponding
<script> tags via the extrahead template block in
source/_templates/layout.html. Now, math formulae and equation can be
displayed in the glossary tooltips even if the parent *.rst page does not
contain any math.
The glossary tooltips are positioned automatically in a way that they are displayed within the viewport borders. However, since MathJax rendering takes a moment, a glossary tooltip may subsequently grow beyond the viewport borders after initial positioning.
Similarly-styled tooltips are also used to replace the normal plain ones for
:abbr:.
These glossary tooltips look like this in action: The type-1 error is related to the CL.
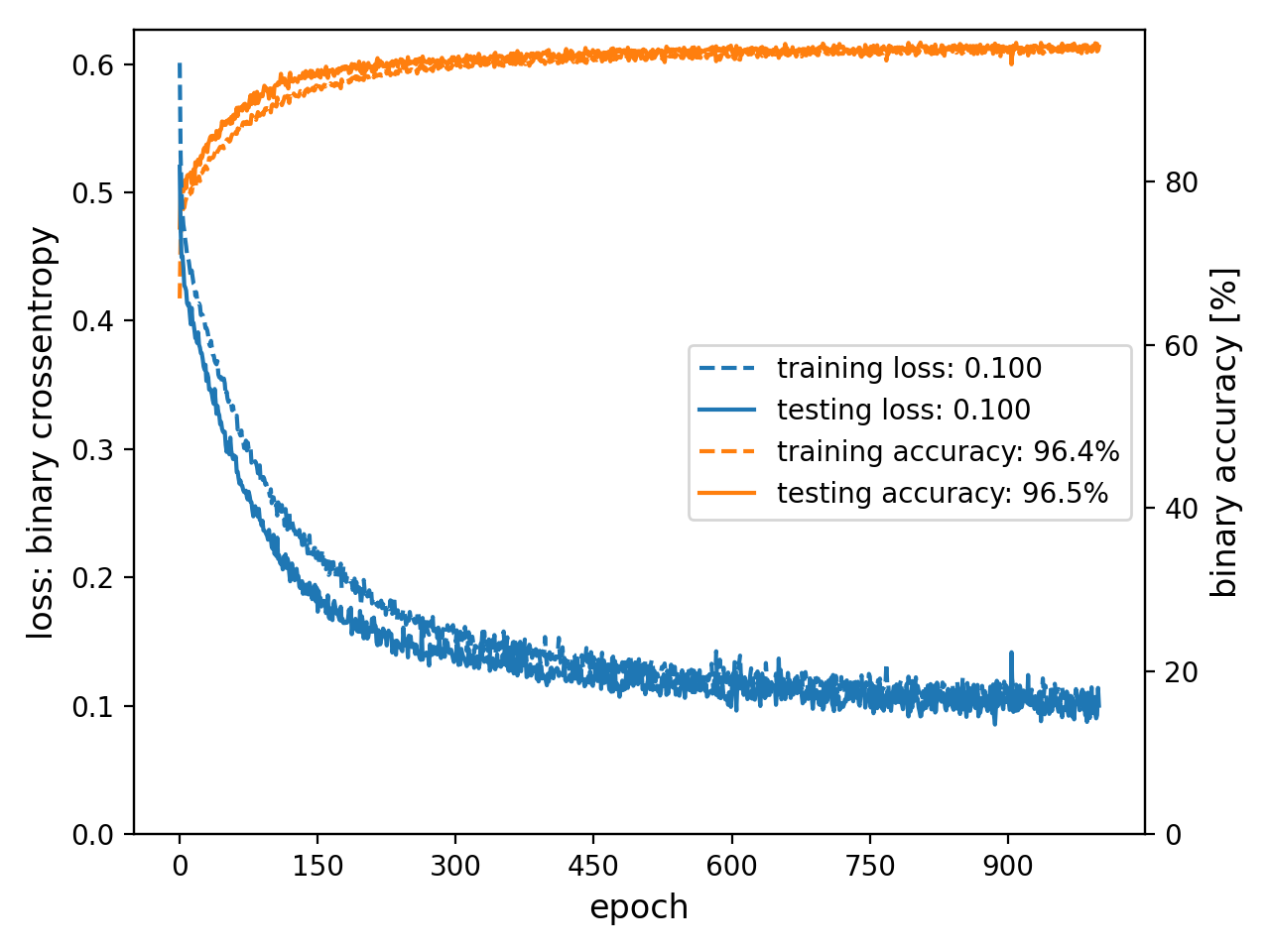
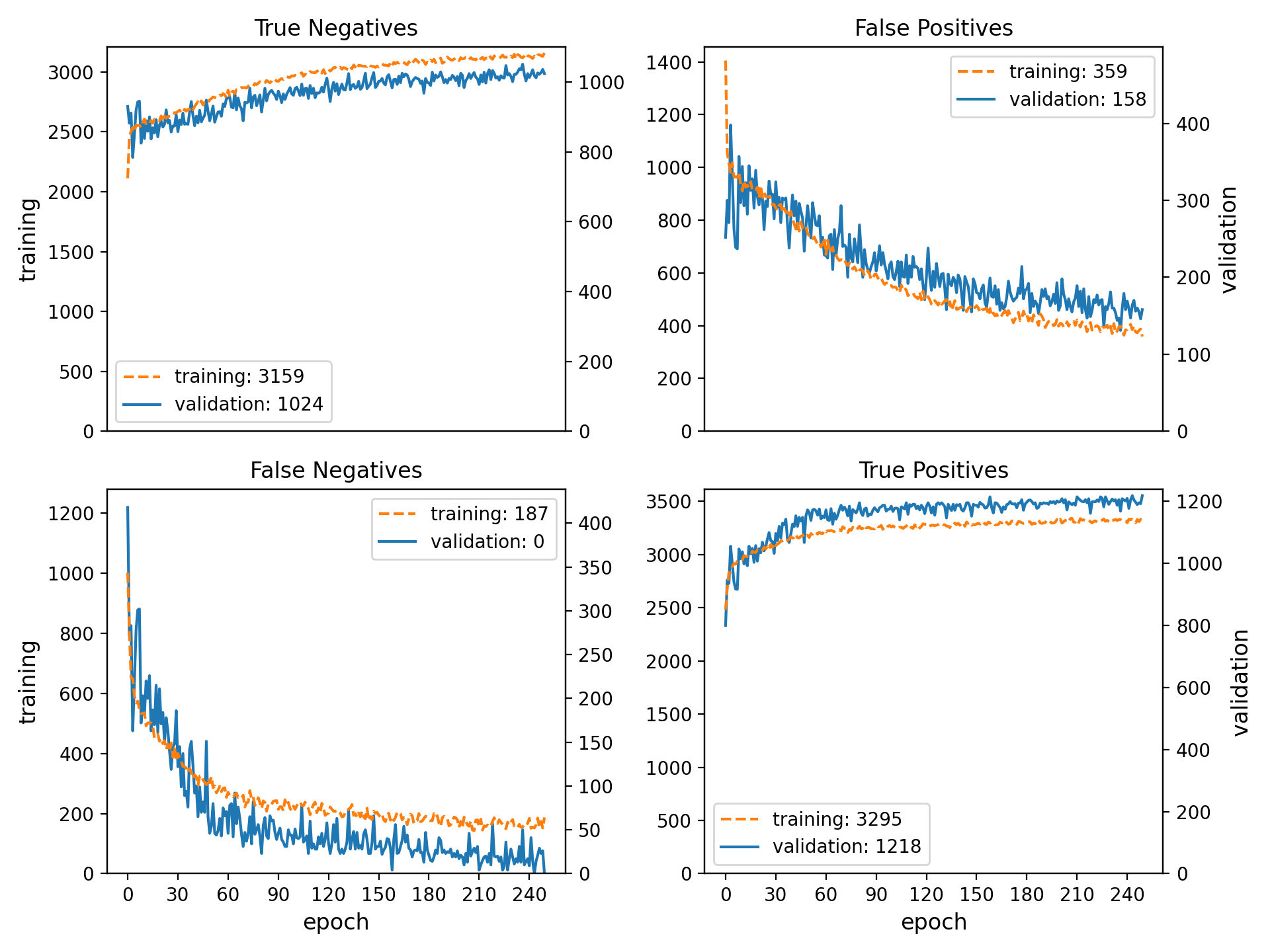
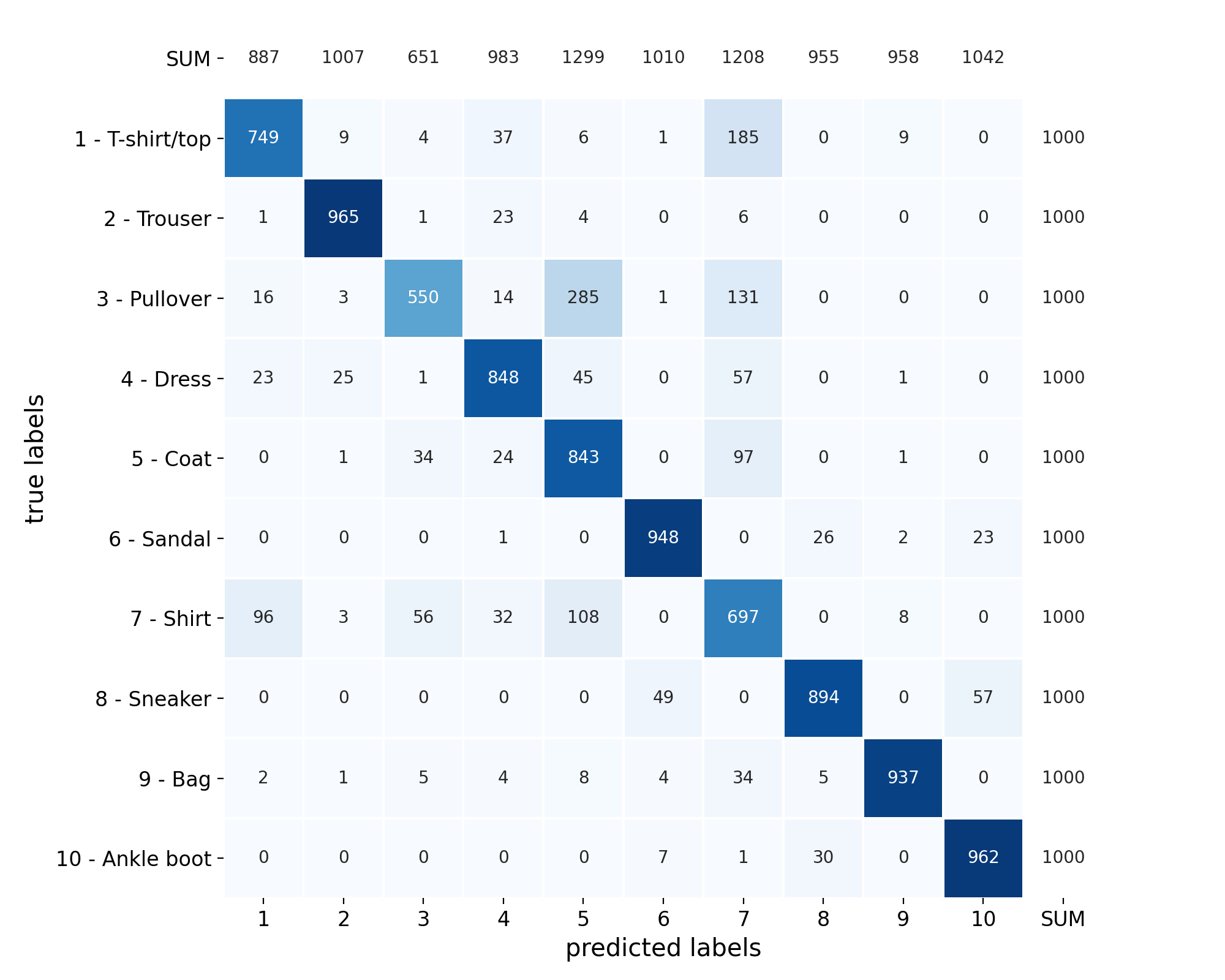
Plot Galleries#
Horizontally Scrolling Gallery#
Definition
.. list-table::
:class: spellbook-gallery-scroll
* - .. figure:: /images/plot_grid_1D.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/loss-acc.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/true-false-pos-neg-rates.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/rec-prec.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/roc.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/confusion-matrix-absolute.png
:height: 200px
The table of plots will be scrollable horizontally if it is wider than the window. Otherwise, the plots will be centered horizontally.
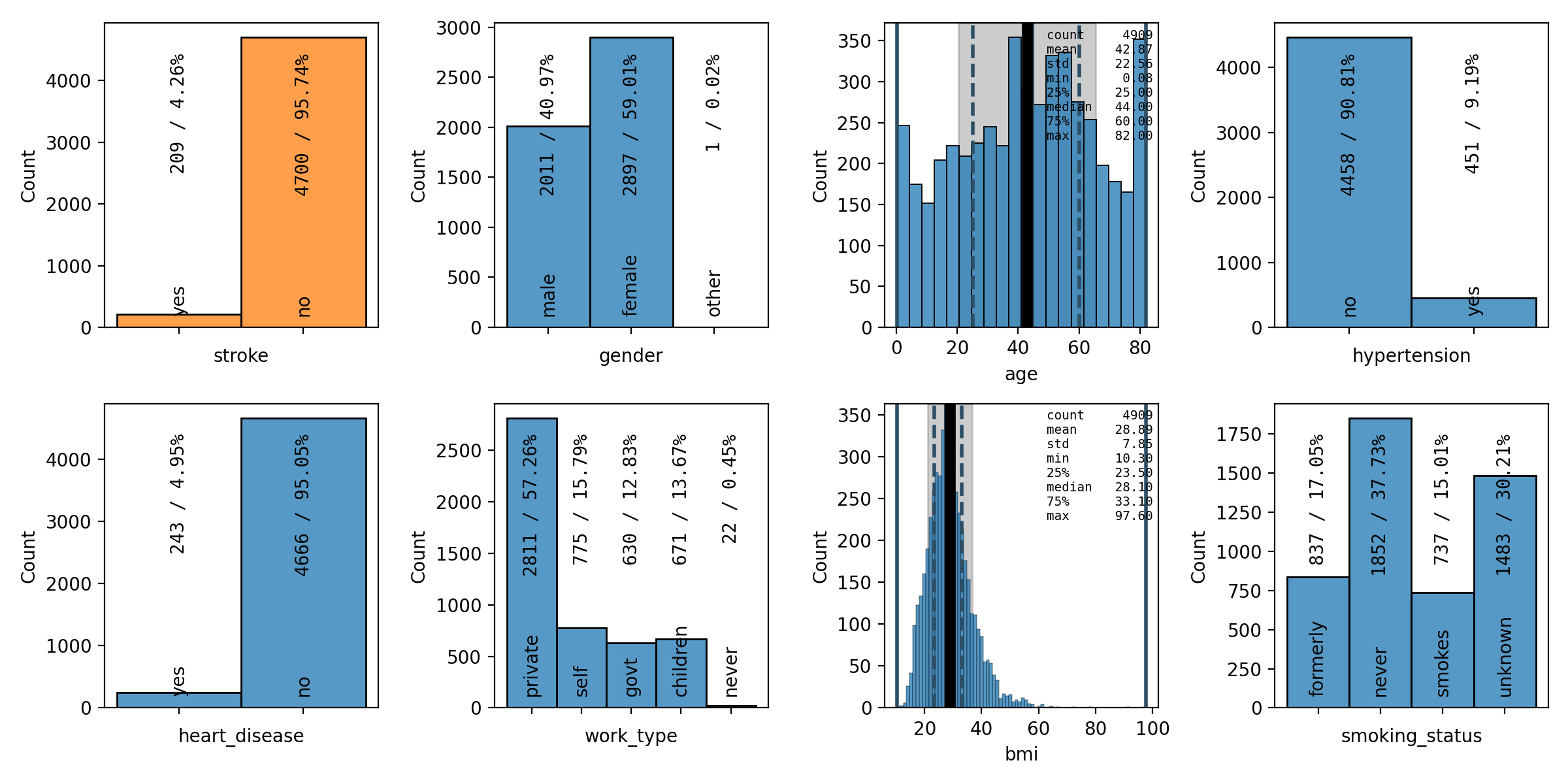
|
|
|

|

|
|
Wrapping Gallery#
Definition
.. list-table::
:class: spellbook-gallery-wrap
* - .. figure:: /images/loss-acc.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/true-false-pos-neg-rates.png
:height: 200px
- .. figure:: /images/roc.png
:height: 200px
The table of plots will be wrapped into the next lines if it is wider than the window. Otherwise, the plots will be centered horizontally.

|

|

|
Styling#
page covering the full width of the viewport
consistent custom colour scheme
footnotes entries in the same line as the footnote mark in footnote lists
horizontal lines underneath the
<h2>and<h3>headersthe previous/next buttons at the bottom of each page
borders around functions, classes and methods in the source code reference
fully qualified names for modules, including the
spellbookprefix, in the auto-generated source code documentationthe Extras toctree in the left side bar with pointer to the ToDo list, the glossary and the index
links to GitHub and LinkedIn at the bottom of the left sidebar
