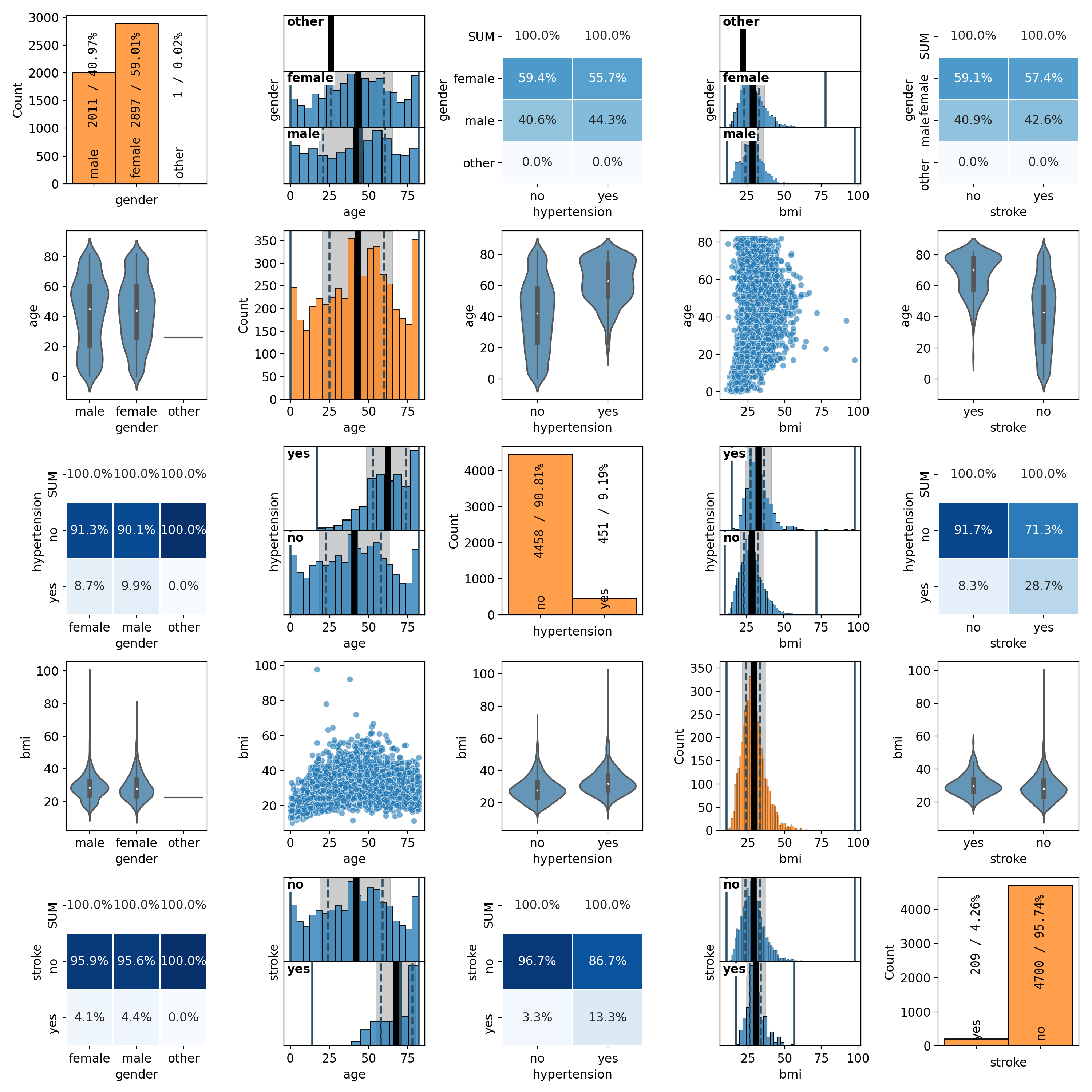
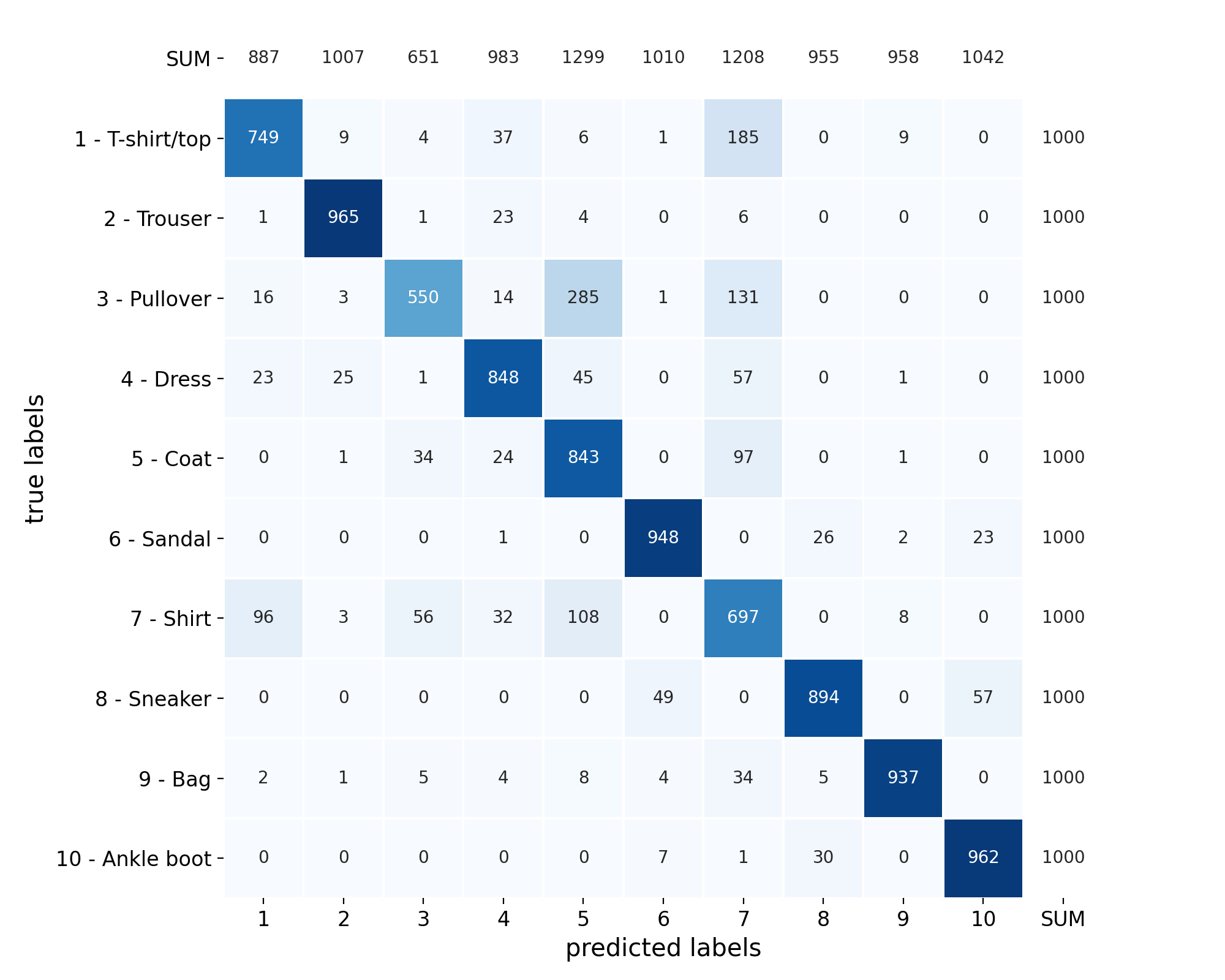
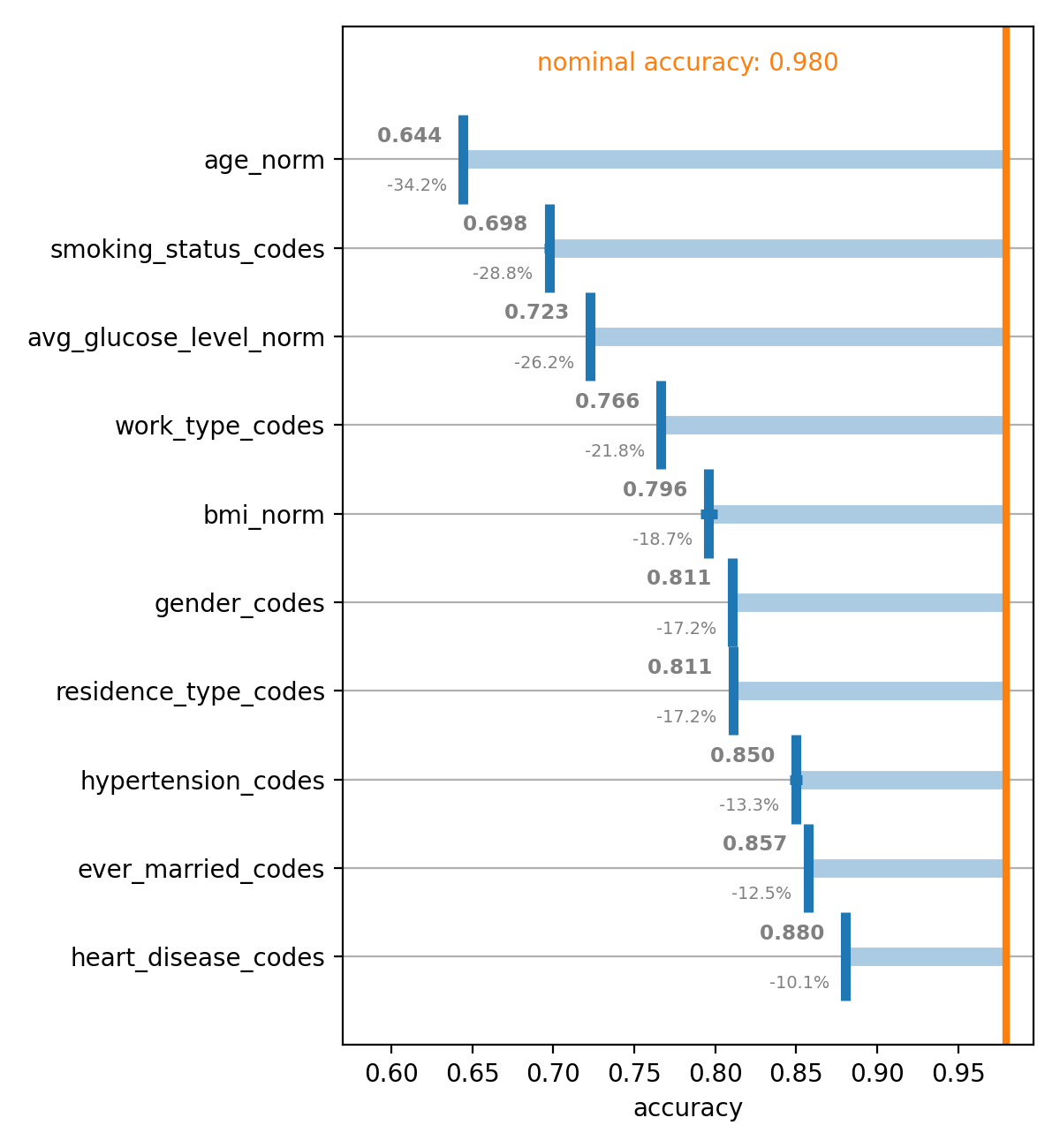
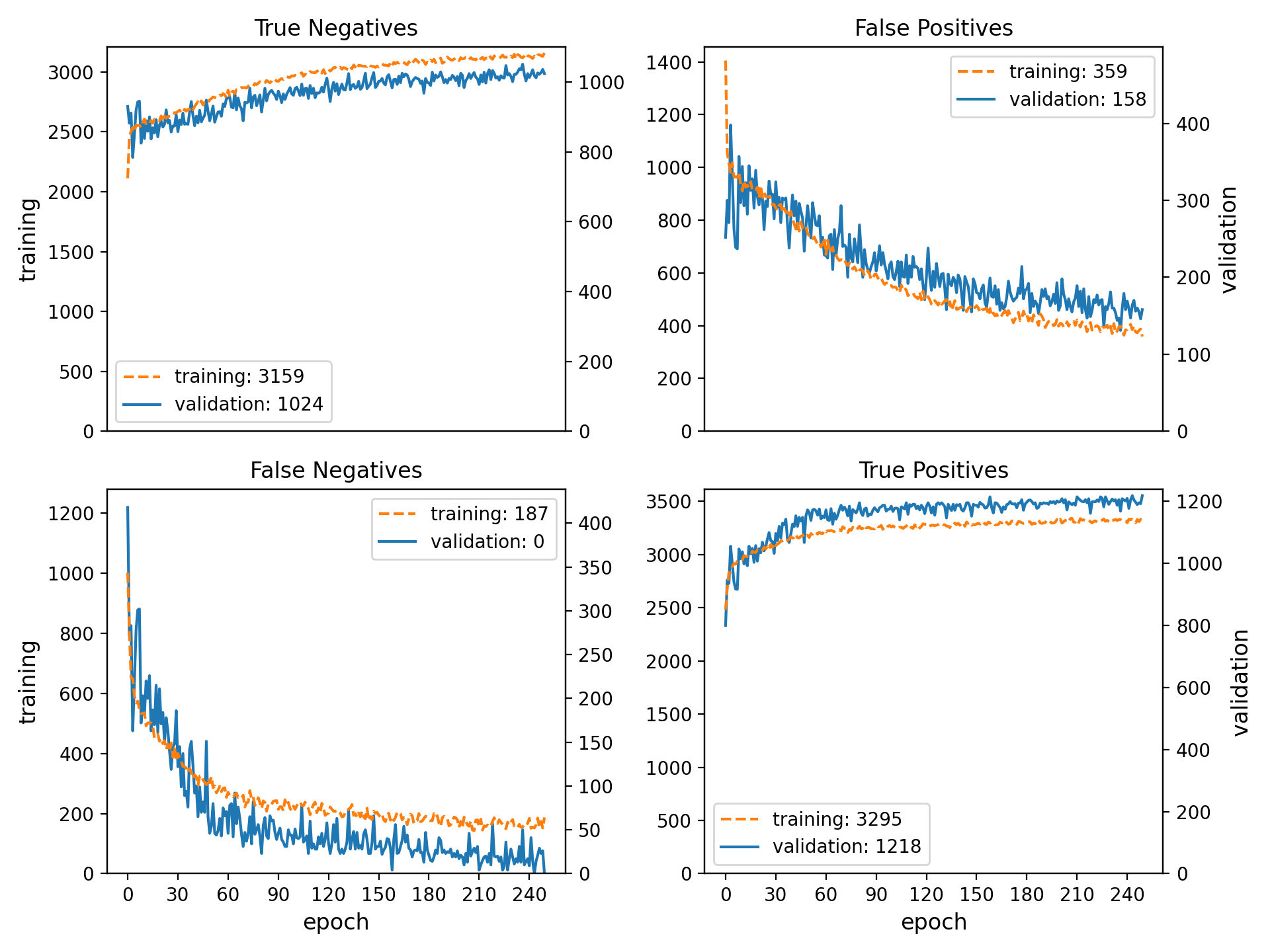
Welcome to the spellbook Data Science & Machine Learning Library!
Contents
Welcome to the spellbook Data Science & Machine Learning Library!#
Why spellbook?
spellbook contains classes and functions to boost productivity in the area of data science and machine learning.
It also features a projects & tutorials section which will be further populated over time. These projects and tutorials serve both to explore and learn about data science and machine learning tools and techniques as well as to provide hands-on examples for how to use the spellbook library.
Projects & Tutorials
spellbook is where I collect functionality that I implement and expect to reuse later. In this spirit, spellbook grows as needed and its development does not aim to complete a specific set of features. The repository is structured as follows:
doc/: Sphinx documentation includingsource code / API documentation
assorted notes on tools and technologies
examples/: Projects and tutorialsspellbook/: Python modulesspellbook.input: functions for data preparation and input pipeliningspellbook.inspect: functions for model inspectionspellbook.plot: high-level functions for creating and saving plotsspellbook.plot1D: low-level functions for creating 1D plotsspellbook.plot2D: low-level functions for creating 2D plotsspellbook.plotutils: helper functions for the other plotting modulesspellbook.stat: statistics helpersspellbook.train: functions for model training and validation
Installation#
spellbook is available via its GitHub repository. You can clone it with
$ git clone git@github.com:dmrauch/spellbook.git
spellbook depends on Python as well as a number of tools and packages built for and on top of Python, most notably
Matplotlib (
matplotlib) → https://matplotlib.org/NumPy (
numpy) → https://numpy.org/pandas (
pandas) → https://pandas.pydata.org/scikit-learn (
sklearn) → https://scikit-learn.org/stable/SciPy (
scipy) → https://scipy.org/seaborn (
seaborn) → https://seaborn.pydata.org/TensorFlow (
tensorflow) → https://www.tensorflow.org/
These and the other dependencies can be installed via the included Anaconda
environment requirement file spellbook.yml. Therefore, it is
recommended to install Anaconda. Afterwards you can
do:
$ cd spellbook
$ conda env create --file spellbook.yml
which will create an Anaconda environment called spellbook and install
the configured packages into it. This environment will be located in the
envs/ folder in your Anaconda installation.
If you want to use Jupyter notebooks, please activate the environment and register it with the Jupyter service:
$ conda activate spellbook
$ python -m ipykernel install --user --name=spellbook
To make this package available on your system, do the following:
Add the repository’s root folder to your
$PYTHONPATH, e.g. via your.bashrc:export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:/path/to/repository/spellbook
Then you can import spellbook modules with
import spellbook as sb
Alternatively, e.g. in a Jupyter notebook, add the repository’s root folder to the system path:
import sys sys.path.append('/path/to/repository/spellbook')
To compile the Sphinx documentation including the API reference and the notes, do
$ cd doc
$ make html
The documentation is then built in doc/build/html/.
Usage#
When you want to use spellbook after installation, just activate the Anaconda environment:
$ conda activate spellbook
Development#
Some of the docstrings of the Python functions include doctest code snippets with examples that are shown in the source code documentation. These examples can be run as tests with
$ cd doc
$ make doctest
Publishing of the Compiled Documentation to GitHub Pages#
Note
The Sphinx documentation is automatically built and published via the GitHub Action
configured in .github/workflows/sphinx-publish.yml when a commit is pushed to the
publish branch - i.e. changes should be merged from master into publish and then pushed
to GitHub.
The automated build makes use of the requirements.txt. This is due to the fact that the
GitHub action sphinx-notes/pages accepts a pip requirements file. Creating the conda
environment on the runner and listing it into a requirements file led to errors when
sphinx-notes/pages tried to install the dependencies. Therefore, the requirements.txt
now has to be kept in sync with conda’s spellbook.yml manually until a better solution is
in place.
The old manual procedure
clone the repository to a different folder
git clone git@github.com:dmrauch/spellbook.git spellbook-gh-pages
create the new branch
gh-pagesgit branch gh-pages
The new branch is created but the original branch remains active and checked out. Switch to the new branch with
git switch gh-pages
compile the documentation in the original folder using the proper
masteror feature branch and then copy it over to the folderspellbook-gh-pagespush the compiled documentation to the branch
gh-pageson GitHubgit push -u origin gh-pages