spellbook.inspect
Contents
spellbook.inspect#
Functions for model inspection
- Classes:
|
Feature importance from permutation |
Classes#
PermutationImportance#
- class spellbook.inspect.PermutationImportance(data, features, target, model, metrics, n_repeats=10, feature_clusters=None, tfdf=False)[source]#
Feature importance from permutation
This implementation follows the Permutation Feature Importance algorithm in scikit-learn
presented in the scikit-learn User Guide
implemented in
sklearn.inspection.permutation_importance()
but goes further in that it provides a mechanism for permuting clusters of multiple features simultaneously. This allows to estimate the permutation importance when some of the feature variables are correlated.
- Parameters
data (
pandas.DataFrame) – The datasetfeatures – The names of the feature variables
target – The name of the target variable
model (
tf.keras.Model) – The predictor/classifier/regressormetrics ([
tf.keras.metrics.Metric]) – The metrics to evaluaten_repeats (
int) – How often each feature (cluster) is permutedfeature_clusters (
typing.Optional[typing.Dict[str,typing.List[str]]]) – Optional. Dictionary with cluster names as keys and lists of features as the values. Each list contains the features that are grouped together as one cluster and permuted simultaneously.tfdf (
bool) – Optional. Whether or not the model is one of the models intensorflow_decision_forests
- baseline#
Dictionary containing the nominal metrics, i.e. without permutation. The keys are the names of the metrics and the values are the values of the metrics.
- results#
For each feature or feature cluster, a dictionary is added to the list. Each dictionary has the following keys and associated values:
feature: The name of the feature or the feature clusterresults: A list containing a dictionary for each permutation. Each dictionary contains the names and values of the metrics calculated in that permutationmean: A dictionary containing the means of the results, with one entry for each metricstd: A dictionary containing the standard deviations of the results, with one entry for each metricmean_rel_diff: A dictionary containing the relative differences between the mean and the nominal, with one entry for each metric
See also
scikit-learn example: Permutation Importance with Multicollinear or Correlated Features
Methods:
__init__(data, features, target, model, metrics)plot(metric_name[, xmin, xmax, ascending, ...])Plot the permutation importance of features / feature clusters
- __init__(data, features, target, model, metrics, n_repeats=10, feature_clusters=None, tfdf=False)[source]#
- plot(metric_name, xmin=None, xmax=None, ascending=True, annotations_alignment='left', show_std=False, show_rel_diffs=True, rainbow=False)[source]#
Plot the permutation importance of features / feature clusters
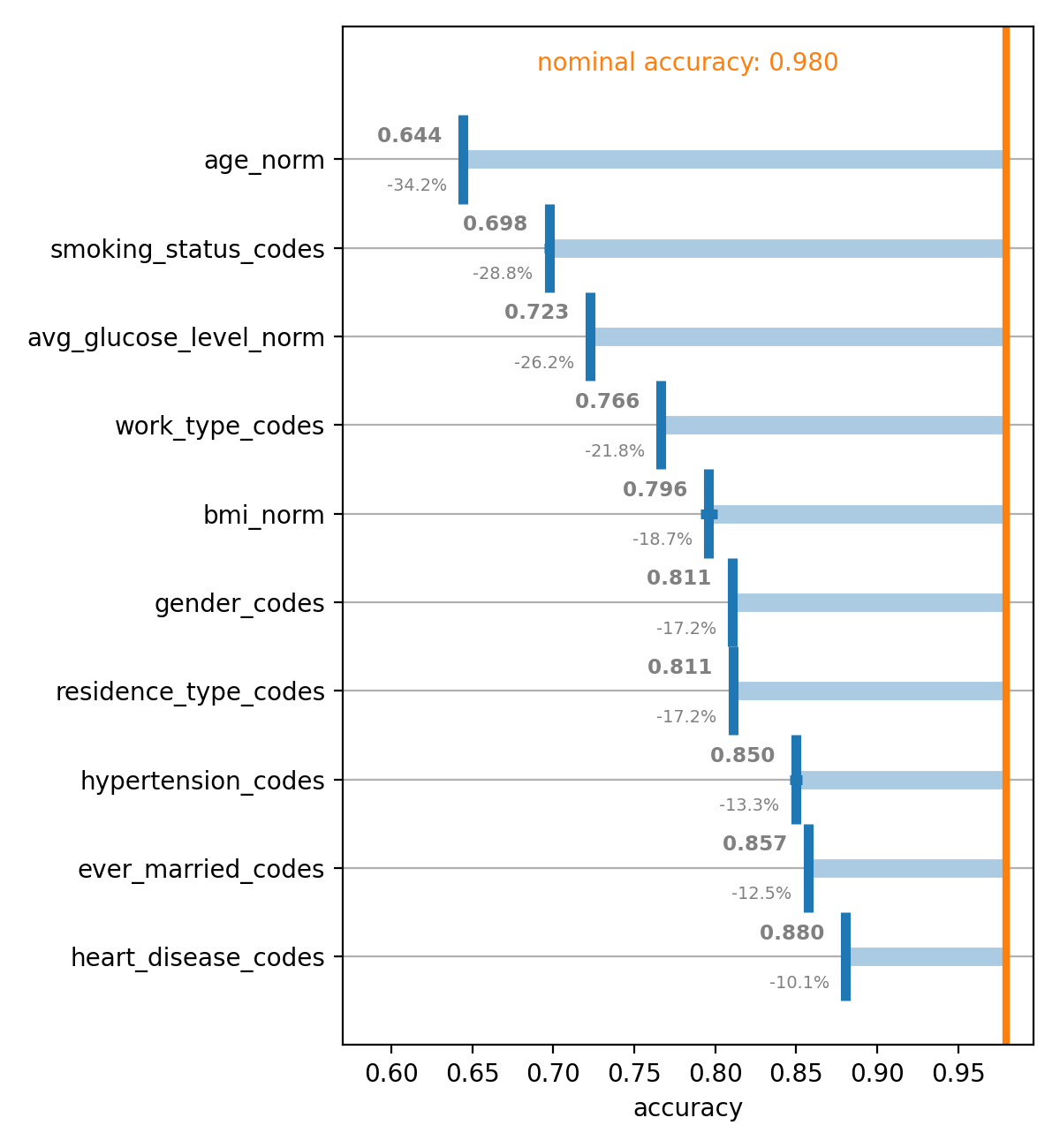
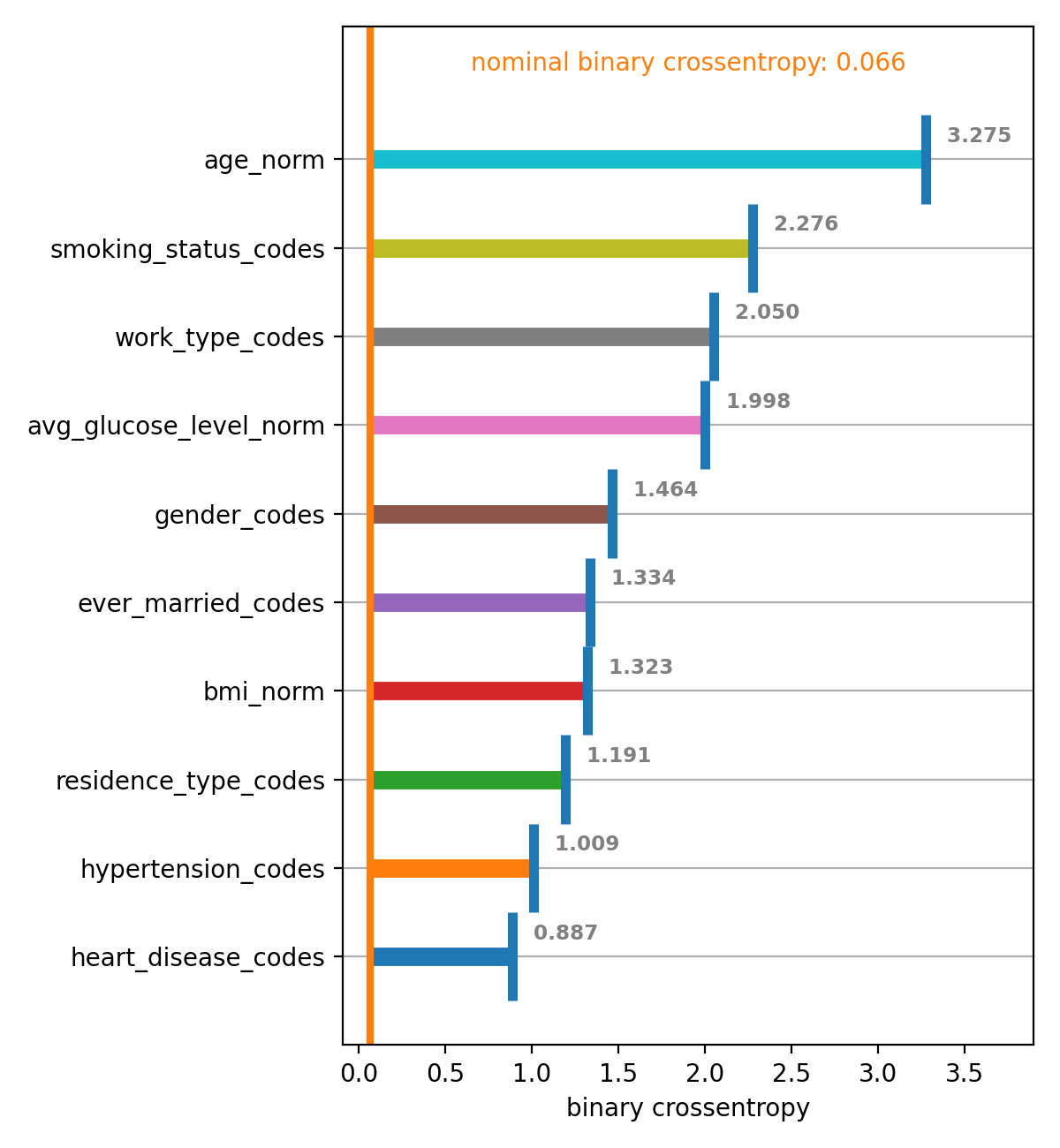
- Parameters
metric_name – The name of the metric to be plotted
xmin (
typing.Optional[float]) – Optional. The lower end of the x-axisxmax (
typing.Optional[float]) – Optional. The upper end of the x-axisascending (
bool) –Optional. Order from the top to the bottom of the plot:
True: Ascending from smaller to larger valuesFalse: Descending from larger to smaller values
annotations_alignment (
str) – Optional. Whether the annotations indicating the mean (and possibly the standard deviation) as well as the relative difference to the nominal metric should be printed to theleftor therightof the markers.show_std (
bool) – Optional. Whether or not the standard deviations of the metrics for the permuted features should be included in the annotations.show_rel_diffs (
bool) – Optional. Whether or not the relative differences between the mean of the metrics for the permuted features and the nominal metric shown be included in the annotations.rainbow (
bool) – Optional. Whether or not the horizontal bars between the means of the metrics for the permuted features and the nominal metric should cycle through the colour palette.
- Return type
- Returns
The figure containing the ranking of the features according to their permutation importance
